Emotion Regulation at Work
People experience many emotions in their lives, both at work and outside of work. Emotions are determinant in many areas from individual processes to interpersonal relationships and they are one of the important tools that people use to understand the world. Emotions can affect people's perspective, morale, and performance positively or negatively. Moreover, if people are managed well, they increase morale and performance.
Emotions are shaped by experiences in people's pasts; intense feelings about an event or entity. It has a stimulating effect in the face of events. For example, sadness makes it easier to seek solutions. Anger in the face of an undesirable event allows reacting quickly. Happiness, anger, sadness, fear are the first emotions that come to mind, and emotions are divided into negative and positive. Emotions that give pleasure and make the person feel comfortable are positive; The emotions that cause discomfort are negative.[i] However, this does not mean that negative emotions should not exist. On the contrary, it is not negative emotions that are bad, but neutral[ii] emotions, which is an undesirable situation. While feeling negative or positive emotion brings with it action, neutral emotion creates insensitivity. It's not just the presence or absence of positive emotions that counts, but rather people's ability to manage and regulate emotions. Reacting appropriately to events and interpreting events as they are is related to emotion management.[iii] When emotions are not properly managed, the world can be more complex and corrosive than it is. We need to stay emotionally balanced to both perceive the world more realistically and protect our psychological health. This can also be called “emotion regulation”.
Emotions are also very effective in working life and are a subject that needs to be examined. It is effective in many aspects, from job satisfaction to decision-making skills. (See Figure 1) For this reason, preventing the problems caused by emotions in working life and protecting the well-being of the employees is possible with the development of the emotion regulation skills of the employees. Emotion regulation/emotion management is defined as controlling the emotional experience that affects the time of occurrence of felt emotions, their severity, and how they are expressed. Regulating emotions allows managing the reactions after experiencing an emotion and to give appropriate reactions[iv]. It is also very important for the volatile, stressful, and uncertain nature of the business world. In terms of both the well-being of the employees and the performance of the institutions, the issue of emotion and emotion regulation in the workplace emerges as a subject to be considered. In business life, employees who have good emotion management, as well as professional skills, are sought.
Figure 1: Mood at Work
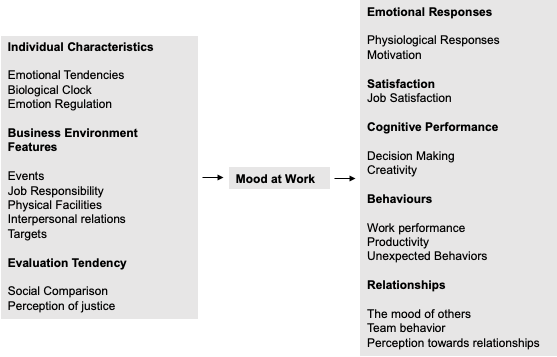
Emotion regulation skills bring many positive results in business life for employees. Employees with high emotion regulation skills can be more flexible in their work. His relations with his teammates are more harmonious and he can manage crisis situations more easily. Those who are successful in emotion regulation are also beneficial for organizations. In corporations where emotions are managed correctly, earnings and strategic growth increase. Although emotion regulation may seem like an individual skill, there are many factors that affect emotion regulation in the workplace and enable it to develop. Organizational environment, job characteristics, and individual differences affect emotion management in workplaces. How the workplace manages emotions and how much employees contribute to emotion management is also related to the emotion climate management strategy of the institutions. Emotional climate management affects the emotions of employees and therefore the emotional health of the organization. A few managements that managers can do for emotional climate management can be listed as follows. [v][vi]
Being a role model in calmness and stress management: Managers who take daily stress breaks, communicate their well-being priorities, and model positive behavior through daily actions encourage their teams to do the same.
Meeting employees individually and emotional maps: It is important to understand what is important to each employee, and to recognize their emotional characteristics.
Talking about emotions: It will be beneficial to create environments where your employees can express their emotions.
Giving importance to personal development: Ensuring the development of your employees in emotion management provides corporate development. The development of managers is also important.
Institutions can have healthy emotional climate management by accepting that the emotions of the employees affect the work processes and by investing in studies that will improve the emotion management skills of the employees. Thus, a healthy work environment can be created by reducing the problems caused by emotions in the workplace.

References
[i] Weiss, Howard M.; Russell Cropanzano (1996), “Affective Events Theory: A Theoretical Discussion of the Structure, Cases and Consequences of Affective Experiences at Work”, Research in Organizational Behavior, Vol. 18, ss. 1-74.
[ii] Doğan, Y., Özdevecioğlu, M. (2009). Pozitif ve Negatif Duygusallığın Çalışanların Performansları Üzerindeki Etkisi. Sosyal Ekonomik Araştırmalar Dergisi, 9(18), 165-190.
[iii] Okutan, E., & Karadeniz, S. Duygusal Zekâ ve İlişki Yönetimi. Seçme Yazılar-III, 151.
[iv] Onat, O., & Otrar, M. (2010). Bilişsel duygu düzenleme ölçeğinin Türkçeye uyarlanması: Geçerlik ve güvenirlik çalışmaları. MÜ Atatürk Eğitim Fakültesi Eğitim Bilimleri Dergisi, 31, 123-143.
[v] Akçay, C., & Çoruk, A. (2012). Çalışma yaşamında duygular ve yönetimi: Kavramsal bir inceleme. Eğitimde Politika Analizi, 1(1), 3-25.