Social Performance Management
With the UN Sustainable Development Goals published in 2016, studies that benefit society in addition to financial purposes in work-life have started to become widespread. The social missions of the organizations have gained importance as much as their financial goals. Service buyers and stakeholders are now interested in the financial return of the companies they will do business with, as well as the value they add to the society, which puts service buyers in the center, cares about their social needs. It turns to alternatives that offer different collaborations within the framework of its social missions.
Social missions are purposes other than financial targets that provide benefits to the society, economy, and/or environment of organizations in various ways, that support targets that are sensitive to the needs and expectations of service recipients. Having a social mission is a way to contribute to society in a meaningful way. When communities are supported and individuals are empowered through social benefit, this positive change paves the way for business growth and the development of organizations. For example, the aim of a fresh food factory to facilitate the access of people with limited access to food is an example of a social mission. Within the framework of this mission, the support given to social development ensures the development of the entire business world together with society.
In the continuation of creating a social mission, organizations need to make plans and studies in line with this mission and get results. The results obtained as a result of the studies carried out in accordance with the social mission and the evaluation of these results are called social performance. Social performance management (SPM), on the other hand, includes setting social goals, strategies to achieve these goals, analysis of strategies, relevant outputs, and monitoring and reporting of positive changes in society and the lives of service recipients. [1] In this way, changes in service recipients and society and the goals achieved can be analyzed. SPM is essential to sustaining the social mission.
SPM is beneficial for service recipients and organizations as well as for the benefit of society due to the continuation of the social mission. SPM provides transparent management and service buyers the opportunity to express their expectations and establish different business partnerships besides financial gain[2]. For example, a microfinance organization operating in the Philippines[3] has a social performance department with the mission to eradicate poverty and carries out systematic studies on this. It also allows service buyers to participate in the work of this department and gain added value. [4]
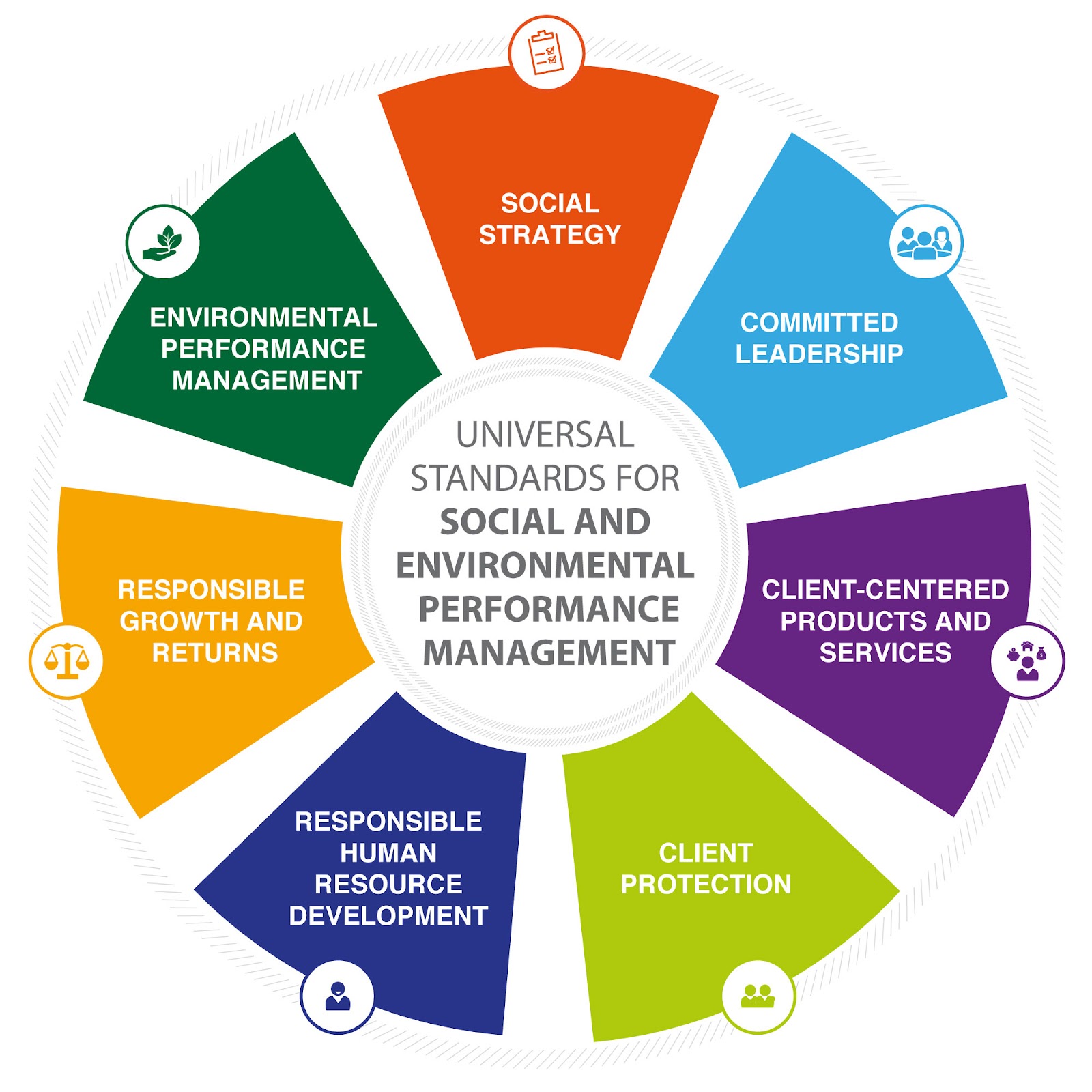
According to The Social Performance Task Force (SPTF)[5], SPM consists of seven steps. (See Figure 1). These steps are briefly as follows.
Social Strategy: A strategy for achieving the provider's social goals is determined. The organization collects, analyzes, and reports specific data in line with these objectives.
Responsible Leadership: Management plays an active role in achieving social goals and follows the studies.
Customer-Oriented Products and Services: Products are developed according to the expectations of the customers. Developed studies benefit customers.
Protection of Customers: Customers do not participate in activities they do not plan financially. Customers are informed of all steps of the work done.
Development of Responsible HR[6] Studies: The HR system is created to support social strategy. A fair and safe working environment is provided.
Responsible Growth and Earnings: While the organization is growing, it acts in accordance with its social strategy and does not work to put its customers at risk.
Environmental Performance Management: Changes originating from the environment are followed. It sets environmental targets and carries out these in an integrated manner with its social performance.
Figure 1: Social Performance Task Force (Universal Standards of the Social Performance Task Force)
One of the most important stages in SPM is analysis, information gathering, and reporting. Any application that is not measured and tracked cannot be managed. Operations are created within the framework of the social mission and strategy. It is applied and analyzed. In each new study, new needs of the stakeholders and the organization are determined and new operations are created. Thus, loss of time and effort is prevented. The continuity of the social mission is ensured and the needs of the stakeholders are responded to in a short time. Social performance flow in SPM can be modeled as follows (See Figure 2).
Figure 2: Social Performance Flow[7]

Within the scope of SPM decent work and economic growth, the importance of organizations in terms of development and sustainability goals is increasing.[8] Collaborations, in which organizations will meet within the framework of social mission as well as financial partnerships, and efforts to establish a balance of profit and benefit will become even more visible in the coming period.

References
[1] ECLOF International (2018), Socıal Performance Management In A Purposive Way. https://eclof.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/ECLOF-SPM-Framework-Document.pdf
[2] Waddock, S. A., & Graves, S. B. (1997). The corporate social performance–financial performance link. Strategic management journal, 18(4), 303-319.
[3] Microfinance is the delivery of financial services to low-income clients or credit solidarity groups, including consumers and self-employed, who have traditionally had no access to banking and related services.
[4] The SEEP Network (2006). Social Performance Management. Social Performance Progress Brief, 1(2).
[5] The Social Performance Task Force (SPTF) is a non-profit membership organization with more than 4,400 members from around the world. Our members come from every stakeholder group in inclusive finance. SPTF works with these stakeholders to develop and promote standards and good practices for social performance management (SPM) to make financial services safer and more beneficial for customers.
[6] Human Resources
[7] The SEEP Network (2006). Social Performance Management. Social Performance Progress Brief, 1(2).
[8] https://www.convergences.org/en/social-performance-management-is-becoming-mainstream-an-opportunity-or-a-threat-for-the-impact-investment-sector/