Time Management and Prioritization
Success is achieved when we understand the value of time and can use it in the most efficient way. In this fast-paced age, managing time effectively and setting priorities is of vital importance for each of us. But often we have to balance different areas of our lives and put urgent tasks before important tasks. In this blog post, we will discuss time management and prioritization issues, exploring ways to identify critical tasks, increase efficiency, and use our time more effectively.
Time is a concept with multiple definitions. By some definitions, sharp and clear; According to some definitions, it is subjective and variable. This concept is discussed in three types. Physical, biological and psychological time. Physical time is a type of time that can maintain its continuity, can be measured by a clock, and continues from the past to the future. Biological time is a type of time that is controlled and measured by biological clocks, which is effective in the realization of biological processes by ensuring the continuity of the organs that determine a large part of our lives. The similarity between physical time and biological time is that they are both continuous. Psychological time differs from the other two types of time in that it can be evaluated through awareness and consciousness. Psychological time is not a continuous flow but consists of discrete measurements. In other words, psychological time consists of units of time called psychological moments, and these times are not chronologically ordered.
Time management is the process of using time effectively and efficiently. This process; It applies to business, personal life or any other field of activity. Time management skills help achieve goals, set priorities, and reduce stress.
Factors that hinder time management are examined in two groups: factors arising from the person himself and factors arising from external factors. In order to manage time, these factors must first be determined correctly and preventive and interventional studies must be carried out for the determined factors. Internal factors that hinder time management include behavioral patterns such as indecision, lack of planning, inability to set priorities, inability to say no, procrastination, overconfidence or insecurity, haste, perfectionism, etc., which originate from the person himself. External factors that make time management difficult include factors such as sudden unexpected tasks, inefficient use of technological communication tools and working environment conditions.
Another benefit of being able to manage time is that it directly affects work-life balance. When time management can be done, work and life balance becomes more satisfying. In the most basic terms, work-life balance; It is the effective management of personal, business and social life.
Work-life balance is expected to be balanced in three separate areas. These areas are time, commitment and satisfaction. Time balance, devoting equal amounts of time to work and family roles; balance of commitment: having equal commitment to work and family roles; Satisfaction balance means feeling equally satisfied with work and family roles. When time management cannot be done properly, work-life balance is disrupted. When time management is evaluated in two separate categories, at work and at home, they affect each other. Disruption of work-life balance can affect an individual's performance, job satisfaction and health. Although failure to maintain work-life balance may seem like a situation with individual effects at first, if not intervened, it can become a psychosocial risk and affect both the individual's family and work life. The work efficiency of individuals who cannot achieve work-life balance decreases and they have difficulty concentrating on their work. Failure to maintain this balance turns this situation into a risk factor over time. If left untreated, it may become a worrying situation for the institution and the individual.
Time management has certain steps. In order to manage time, it is necessary to determine how time has been evaluated so far. This process is only possible with time usage analysis. After analyzing how time is used, it is necessary to define time problems. At this stage, factors that cause time loss are identified. In the next step, the individual/institution needs to define itself. Skills and resources are evaluated, and behaviors that cause time wasting are identified. In the fourth stage, goals and priorities are determined. Goals are determined from general to specific. By determining the main goal and intermediate goals in line with that goal, the fifth stage, which is transferring the program goals to the implementation plans, is started. At this stage, a detailed plan is prepared. During the implementation phase, time management techniques are used. In the last step of the process, the process is analyzed and if there are any points that do not work, it is returned to the previous stages.
Below you can examine some methods that will make Time Management easier:
Pomodoro Technique:
It emphasizes working in focused intervals with regular breaks to maximize productivity. The technique involves dividing work into 25-minute intervals called "pomodoros" and then taking a short 5-minute break.
Jar Theory:
This theory emphasizes prioritization and effective time. For example, imagine a jar representing current time and a variety of rocks, pebbles, and sand representing different tasks and activities. The theory suggests that in order to fit all the items into the jar, the individual must place large rocks first (high priority tasks), then pebbles (secondary tasks), and then sand (less critical activities). This theory demonstrates the importance of identifying and addressing the most important tasks before delving into less critical issues. By prioritizing and allocating time accordingly, individuals can ensure that essential tasks are completed without neglecting smaller tasks.
Parkinson's Law:
It states that any workload expands to fill the time available for completion. In other words, if more time is devoted to a task, the individual is more likely to use all of the time completing the task rather than completing it quickly and using the remaining time for other tasks. This theory emphasizes the importance of setting realistic deadlines and limiting the time allotted for each task. Individuals can consciously set shorter deadlines, improve their focus, increase efficiency, and complete tasks quickly. Parkinson's Law emphasizes that the perception of urgency and limited time can positively affect productivity.
''ALPEN'' Method:
It is a Time Management technique derived from the German word "Alpen" meaning Alp. It is an abbreviation for “Aufgaben” (tasks), “Lange” (duration), “Puffer” (buffer), “Entscheidungen” (decisions) and “Nachkontrolle (after-action review)”. The method emphasizes comprehensive planning and organization of tasks. It involves listing all tasks, estimating the time required for each, adding extra buffer time for unforeseen circumstances, making decisions regarding task priority, and reviewing what has been completed. Additionally, the ALPEN method provides a comprehensive framework for effective task management, allowing individuals to allocate time more healthily, prioritize tasks, and control their schedules.
''ABC'' Method:
The ABC method is a simple yet powerful Time Management technique used for task prioritization. It involves dividing tasks into three groups: A, B and C. 'A' tasks are high priority tasks that have significant consequences if not completed on time. These tasks require immediate attention and should be addressed first. 'B' tasks are those that are important but less urgent. If possible, they can be planned for later or delegated to others. 'C' tasks are low priority tasks that can be postponed or eliminated without significant consequences.
Using the ABC method, individuals can categorize their tasks, improve focus on the most critical activities, and allocate time accordingly. These measures ensure that important tasks are not overlooked or delayed.
And finally the Einsenhower Matrix:
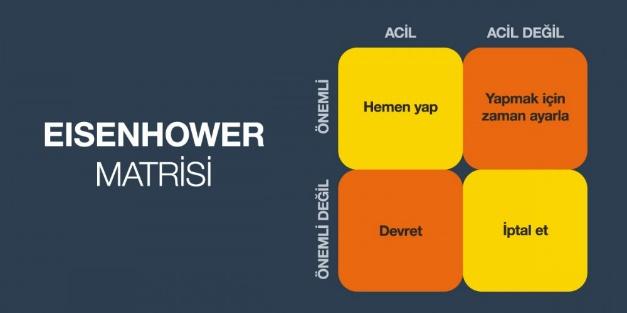
This matrix is a tool that helps individuals prioritize their tasks. The matrix consists of four key quadrants. The first quarter contains important and urgent tasks, such as emergencies or urgent deadlines. These tasks require immediate attention. The second quadrant includes basic but not urgent tasks such as planning, strategy development, and personal development. These tasks should be prioritized and scheduled to prevent them from becoming urgent. The third quadrant consists of urgent but unimportant tasks, such as interruptions, meetings, or distractions. It is crucial that these tasks are minimized or delegated because they can consume time without adding significant value. The fourth quadrant includes tasks that are neither important nor urgent, such as time-wasting activities or excessive social media use. It is best to eliminate or limit these tasks because they provide little or no value.
SOURCE
- Akgemci, T., Çelik, A., Aydoğan, E., Akatay, A., (2003), Time Management and Managerial Time Activity, (Editor: M. Şerif Şimşek, Adnan Çelik), Gazi Kitabevi, Ankara.
- Güçlü, N. (2001). Stress Management. G.U. Gazi Faculty of Education Journal Volume 21, Issue 1 (2001) 91-109
- İşcan, S. (2008). THE EFFECT OF PAMUKKALE UNIVERSITY STUDENTS' TIME MANAGEMENT SKILLS ON THEIR ACADEMIC SUCCESS
- MACKENZIE, R. Alec; Time Trap: How Do You Control Time?, (Translated by: Yakut Güneri), Amacom Interest Publications, Istanbul, 1989
- Şimşek, M., Çelik, A., Akgemci, T., Bakan, İ., Güleş, Aydoğan, E., Taşlıyan, M., Erdem, R., Zerenler, M., Soysal, A., Akatay, A. ., Pınar, H., İleri, Y., Genç, E., Tosun, M. (2009). Time Management and Effectiveness in Managerial Time. Gazi Bookstore.